mirror of https://github.com/tildeclub/site
parent
c1fbaf11c0
commit
10b9f7aa9f
|
|
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
|||
---
|
||||
title: Editing with Emacs
|
||||
author: ohnoitsnoah
|
||||
category: tutorials
|
||||
---
|
||||
<!--- Make a section for Modes --->
|
||||
Emacs in tilde.club
|
||||
===================
|
||||
[Emacs](https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/) is a text-editor that is very capable, but also can be very confusing to new users, so here's a basic guide to working with Emacs.
|
||||
|
||||
Opening Emacs
|
||||
-------------
|
||||
You can open Emacs by typing `emacs` in the shell. This then opens Emacs :D.
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Elements of the Screen/Terminology
|
||||
----------------------------------------
|
||||
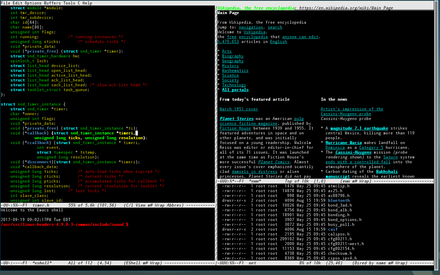
|
||||
|
||||
When first starting Emacs, there are a few elements of the screen that you should know:
|
||||
### Buffer
|
||||
A "Buffer" is basically a container that holds the contents of whatever file you're editing.
|
||||
> "Buffers in Emacs editing are objects that have distinct names and hold text that can be edited."
|
||||
>
|
||||
> -[GNU Emacs 28.2 Manual](https://www.gnu.org/software/emacs/manual/html_node/emacs/index.html)
|
||||
### Window
|
||||
Unlike what Microsoft Windows and other common-place OS' consider "windows", a window in Emacs is more like a window "pane", as where a buffer contains content, a *window* contains a buffer.
|
||||
> "In Emacs terminology, a "window" is a container in which a buffer is displayed. This may be confusing at first; if so, think "pane" whenever you see "window" in an Emacs context until you get used to it."
|
||||
>
|
||||
> -[WikEmacs](https://wikemacs.org/wiki/Emacs_Terminology)
|
||||
### Modeline
|
||||
The Modeline is the strip of details towards the bottom of an instance in Emacs. This shows the file/buffer name, file type, any active modes/extensions, line and column numbers, and more.
|
||||
### Mini-Buffer
|
||||
The Mini-Buffer is the small area under the Modeline. It acts as a prompt, telling you when you've hit the beginning/ending of a buffer, allowing/alerting you to type/confirm commands, and more.
|
||||
### Menu Bar
|
||||
The Menu Bar is the series of drop-down menus at the top of an Emacs instance. It gives all the available commands in the current buffer, and shows their corresponding key-bindings.
|
||||
|
||||
Emacs Command Key
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
<!--- Rename this section --->
|
||||
Emacs has some weird, complex commands, that may not make sense to new users. While this tutorial will mostly be based around using the drop-down menus, it's still good to know how to read command's key-bindings, as using them is the more effective/productive route.
|
||||
|
||||
* `C-` means the Control/Ctrl key
|
||||
* `M-` means the Meta key
|
||||
- While not common on modern hardware, the Meta key can be typed by using either the Escape/ESC key, or the Alt key in some cases
|
||||
* `s-` or `S-` means the Shift key
|
||||
|
||||
Key-bindings in Emacs are typically longer than normal key-bindings used outside of Emacs, usually being a combination of what would be two "normal" key-bindings. For example; to exit Emacs, you can type `C-x C-c`. That means you press both of these key-bindings in series to complete the Emacs key-binding of exiting Emacs. It's very weird and complex, but is easy to adjust to after using it for a while.
|
||||
|
||||
Navigating Emacs with the Drop-Down Menus
|
||||
-----------------------------------------
|
||||
<!--- TODO (Maybe): Talk about using the corresponding key-bindings, maybe in another section(?) --->
|
||||
The way you accsess the drop-downs are by pressing the `F10` key, then using the arrow keys to navigate through the menus. You can press the `F10` key again to exit the menus, or the global "quit" command, `C-g`. As easy as these menus are, I reccommend slowly learning the key-bindings, as they make it faster and easier to navigate through Emacs as a whole. On that note, *I will be putting each commands corresponding key-binding next to their respective section title.*
|
||||
### Switching Buffers (C-x b)
|
||||
When you start Emacs using `emacs` in the shell, you'll be greeted with a welcome screen, along with two other buffers titled `*scratch*` and `Messages`.
|
||||
You can switch between these buffers by going to the Buffers drop-down and selecting which buffer to go to.
|
||||
### Visting a New File (C-x C-f)
|
||||
To visit a new or existing file, simply go to the File menu and select "Visit New File". You may also select "Open file...", however this does the same thing as "Visit New File", just without the ability to create a new file.
|
||||
### Save and Save As (C-x C-s, C-x C-w)
|
||||
To save the current buffer, select "Save" from the File menu. If you need to save the buffer as something else, you can select "Save As", which is also in the File menu.
|
||||
### Killing a Buffer (C-x k)
|
||||
Whenever you are finished working on a file, and no longer need the buffer, you can kill the current buffer by selecting "Close" from the File menu.
|
||||
### Cut, Copy, Paste (C-w, s-c, C-y)
|
||||
Cut, Copy, and Past are all available in the Edit menu.
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue